NASA Project Gemini - Launch Vehicles/Rockets
For Project Gemini, NASA again used modified military ICBMs to reach space, just as they had done for Project Mercury. The newer, more powerful Titan II missile, developed by the US Air Force for the deployment of nuclear warheads, carried the 2-man Gemini capsule into orbit. The unmanned Agena Target Vehicle (which was used as a target for rendezvous and docking maneuvers) was launched atop an Atlas booster.
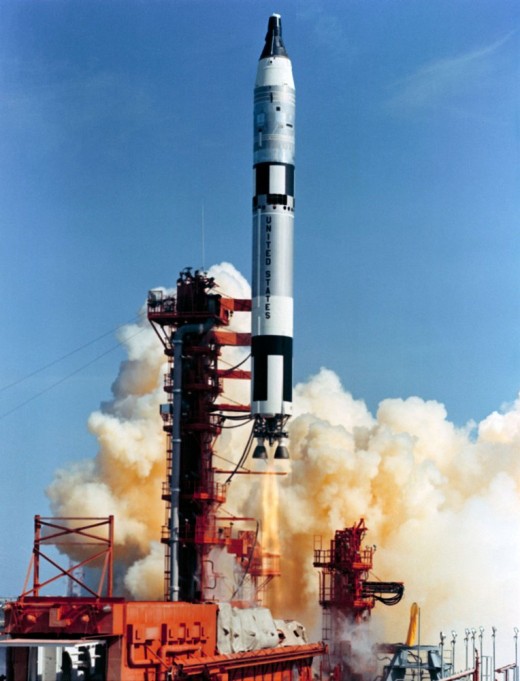

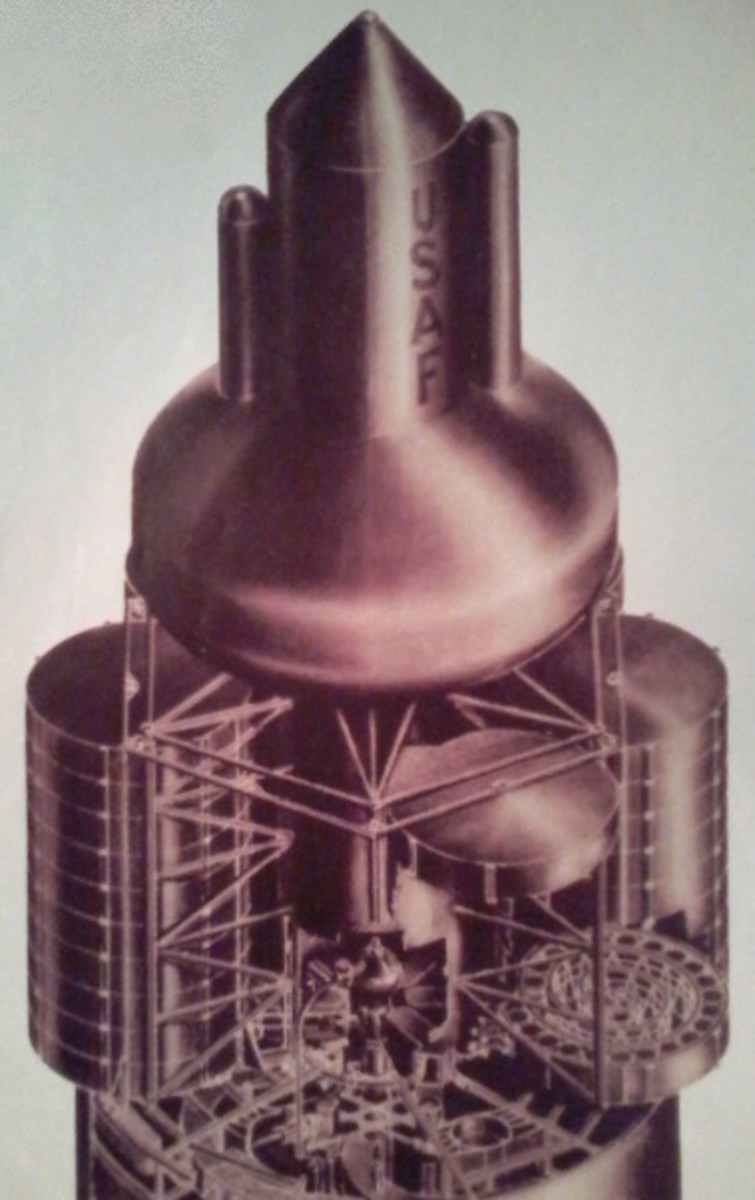
Titan II
The 2-stage Titan II was the first multi-stage rocket used by the US for manned spaceflight. A multi-stage rocket consists of separate sections, or stages, stacked atop one another, each with its own engine and fuel supply. When the fuel from one stage is exhausted, that stage drops off and falls away from the rocket, and the next stage's engine is ignited.
Trade-offs of Rocket Staging
The primary benefit of rocket staging is that an ascending rocket becomes lighter as it discards the unneeded weight of emptied fuel tanks. The remaining fuel can then push the less massive rocket faster and further. This, of course, adds to the complexity (and cost) of the rocket. It also increases the risk associated with a launch, as there is a possibility that a stage's engine will fail to ignite. Gemini required a multi-stage rocket, however, due to the weight of the Gemini spacecraft, which otherwise could not have been accelerated to orbital velocity.
Video: Camera aboard Titan II shows separation of first stage:
Gemini-Titan
Modifications made to the Titan II missile for Project Gemini included the addition of a system to detect and notify the crew of malfunctions, and an inertial guidance system (Titan was radio-controlled when used as an ICBM). Certain system redundancies were added for safety, and elements of the missile that were not needed for Gemini flights were removed.
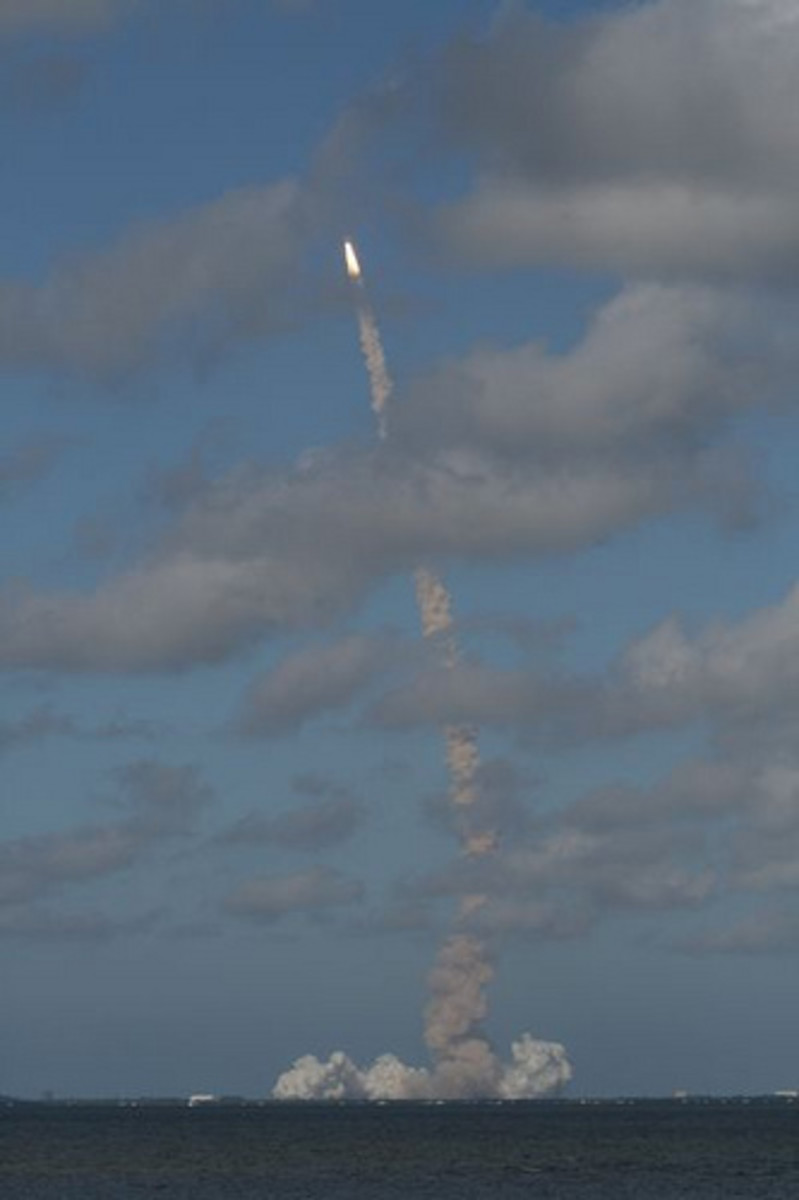
Between April, 1964 and November, 1966, twelve Gemini-Titan missions were launched. Two were unmanned test launches, and ten were manned missions. All were successful. Gemini-Titan launches took place at Cape Canaveral, Florida (then known as Cape Kennedy), from Launch Complex 19.
Atlas-Agena
One of the primary objectives of Project Gemini was the development of rendezvous and docking techniques. NASA needed to master these techniques to have any hope of achieving President Kennedy's goal of a lunar landing within the decade.
Docking
Docking is a procedure in which two spacecraft are physically linked together. In some cases, the electrical systems of the two craft are connected while docked. When docked to the Agena Target Vehicle, for example, the Gemini astronauts could fire the Agena's engine using controls within the Gemini capsule.
The Agena Target Vehicle was developed for this purpose. This unmanned vehicle would be launched separately, and the Gemini astronauts would attempt first to rendezvous with the Agena target, and then dock with it.
Atlas, the US Air Force booster used on all Project Mercury orbital missions, was used to launch the Agena Target Vehicle. All Atlas-Agena launches for Project Gemini took place at Cape Canaveral's Launch Complex 14, the same site as the orbital Mercury-Atlas launches.
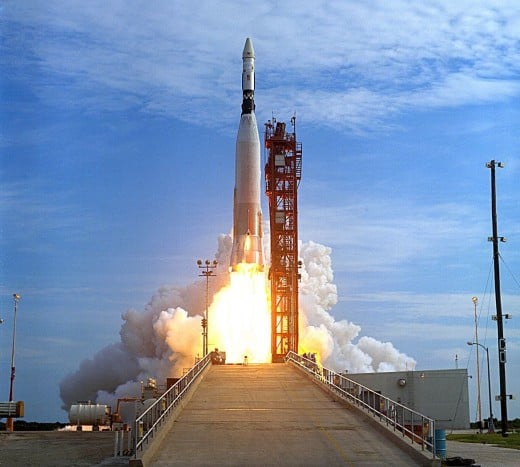

Stage-and-a-half Configuration
Atlas was not a multi-stage rocket, although it did have two smaller rocket engines attached to the sides of the main engine.These engines ignited at liftoff, along with the main engine, and were jettisoned when their fuel was expended.
These engines were not true rocket stages, because they ignited at launch, rather than during flight following the shut off of another engine. This configuration is sometimes known as a stage-and-half configuration.
Titan and Atlas continued to be workhorses for NASA for many years following Project Gemini. Titan and Atlas-based launch vehicles have put numerous satellites into earth orbit, and have launched several unmanned probes to other parts of the solar system - and beyond, in the cases of the Pioneer and Voyager probes.